If you spend any time reading car audio discussions on Facebook or in forums, then you will have undoubtedly come across comments involving the supposed drawbacks of using RCA Y-cables. There seems to be a lot of misconception or misunderstanding about how preamp signals works, and this misinformation leads to comments that aren’t always accurate. Let’s take (more than) a few minutes to clear things up.
If you spend any time reading car audio discussions on Facebook or in forums, then you will have undoubtedly come across comments involving the supposed drawbacks of using RCA Y-cables. There seems to be a lot of misconception or misunderstanding about how preamp signals works, and this misinformation leads to comments that aren’t always accurate. Let’s take (more than) a few minutes to clear things up.
Understanding Preamp Level Audio Signals
 The audio signal that connects your source unit to your amplifier is both very weak and quite small. The voltage of the preamp signal is rarely above 10% of the maximum voltage capability of your source unit for several reasons. Firstly, the signal level is directly proportional to the output of the system. When the volume is low, the signal is low in amplitude.
The audio signal that connects your source unit to your amplifier is both very weak and quite small. The voltage of the preamp signal is rarely above 10% of the maximum voltage capability of your source unit for several reasons. Firstly, the signal level is directly proportional to the output of the system. When the volume is low, the signal is low in amplitude.
The second factor that contributes to the microscopic amplitude of the preamp signal is known as the Crest Factor. By way of a formal definition, the Crest Factor is the ratio between the peak signal amplitude and the RMS value of a waveform. For a pure sine wave, this value would be 1.414. For music, the Crest Factor value is much larger.
We analyzed a few different songs to come up with some relatable numbers. The new song Run by the Foo Fighters has a maximum amplitude of +0.15 dB and an RMS amplitude of -12.7 dB over the entire track. To keep the math simple, let’s call it 13 dB, which is a ratio just shy of 20:1. We also analyzed Heathens by Twenty One Pilots and found that it has a Crest Factor of 10.5 dB, or just about 11.25:1.
If we think about the highest voltage possible on our preamp signal as being 4 volts, then the average voltage for the above track would be 200 millivolts and 355 millivolts respectively. The peak of 4 V only happens when the volume is at maximum. Don’t forget that.
Scotty, We Have No Power!
Another characteristic of our preamp signal is that it contains almost no current flow. As with any electrical circuit, the amount of current flowing through the circuit is determined by the voltage in the circuit and how much resistance there is. The output impedance of most head units is between 300 and 500 ohms. The input impedance on most amplifiers is about 10,000 ohms.
Using our maximum voltage of 4 volts, and a resistance of 10,500 ohms, the maximum current in our circuit will be 0.381 milliamps. If we consider that the average signal amplitude is about 275 millivolts, then we have an average current flow of 0.0275 milliamps. That is nothing.
What does an RCA Y-cable Do?
 An RCA Y-cable allows you to connect a single RCA output to two RCA inputs. Typical applications for Y-cables are a single subwoofer output RCA on a source unit or processor and the need to feed a pair of inputs on a subwoofer amp. Another common application is a source unit with only a single left and right RCA output; you want to use a four-channel amp that doesn’t include a two-input/four-input switch.
An RCA Y-cable allows you to connect a single RCA output to two RCA inputs. Typical applications for Y-cables are a single subwoofer output RCA on a source unit or processor and the need to feed a pair of inputs on a subwoofer amp. Another common application is a source unit with only a single left and right RCA output; you want to use a four-channel amp that doesn’t include a two-input/four-input switch.
Please Don’t Believe the Hype
The biggest myth about the use of Y-cables is that they dramatically reduce the signal going to each input. To prove why this is not true, we need to understand how a voltage divider circuit works. Yes, it is time for a little physics and math.
In an ideal situation, when we have a signal source and a single load, all the voltage developed by the source appears across the load.
If we have multiple loads, the voltage produced by the source is divided among the loads when they are wired in series. In the image below, we have two loads in series with our single signal source.
If the resistance value of the two loads is the same, then the voltage produced by the source is divided equally across the loads. Half the voltage can be measured across each load. Using our 4 V preamp example, we would see 2 V across each load. However, what happens when the load resistance is not the same? We have to do some math to determine how much voltage is across each.
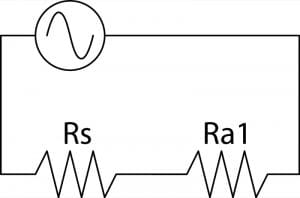
Let’s label the loads. The load on the left will be called Rs. This is the resistance of our source. For this example, we will use a value of 500 ohms. The load on the right will be our amplifier input resistance of 10,000 ohms, and we will call it Ra1.
We have 4 volts being produced by the source and a total circuit resistance of 10,500 ohms. We can calculate that the current flowing in the circuit is 0.0381 milliamps using Ohm’s law. Knowing the current in the circuit allows us to determine how much voltage is dropped across each resistance. For our source load, we have a resistance of 500 ohms with a current of 0.381 milliamps to produce 190.476 millivolts. The rest of the 4 V source signal or 3.809525 volts appears across the load.
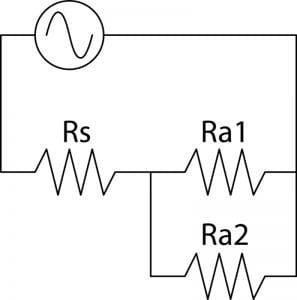
Let’s wire another amplifier in parallel with our first amplifier. This is the same effect as using a Y-cable. Our second amplifier will be called Ra2.
Now it is math time again. This time, our circuit has a total resistance of 5500 ohms, and as such, has a current of 0.7272 milliamps flowing in it. The voltage dropped across the source has increased to 0.363636 volts, and each amp is seeing 3.636 volts. That seems like a noticeable difference, doesn’t it?
The Decibel Scale Changes Everything
Between the two examples above, we have seen a decrease in voltage at the amplifiers by 4.772%. Does that mean our music is almost 5% quieter? No. When we talk about the ratio of voltage to volume, we need to take into account the decibel scale. Our decrease of 4.772% percent in voltage works out to -0.405 dB less output.
Before you get your knickers in a knot, you can fix that by turning the gain on your amplifier up by that amount.
A Worst-case Mathematical Example
 This example was a worst-case scenario. What if you have a source unit with a lower output impedance? Some head units have an output impedance of 300 ohms. For that head unit, with the same 10,000 ohm input impedance on the amplifiers, the change in output by using a Y-cable would be -0.2493 dB. If you have a premium line driver in your system, the output impedance may be as low as 50 ohms. In this scenario, the loss is a paltry -0.0431 dB.
This example was a worst-case scenario. What if you have a source unit with a lower output impedance? Some head units have an output impedance of 300 ohms. For that head unit, with the same 10,000 ohm input impedance on the amplifiers, the change in output by using a Y-cable would be -0.2493 dB. If you have a premium line driver in your system, the output impedance may be as low as 50 ohms. In this scenario, the loss is a paltry -0.0431 dB.
What did we learn from this? If you need to connect many amplifiers to a single source, then choose a source with a low output impedance.
RCA Y-cables as a Solution are Not Evil
If your system requires that you use a set of Y-cables to distribute the audio signal to multiple amplifiers, then go right ahead. Once your installer sets the sensitivity controls on your amps, you will never, ever know they are there.
If you have any questions about the design of your audio system or what to know about how your installer will be wiring it, talk to the salesperson and your local mobile electronics specialist retailer – they would be happy to explain things to you.
This article is written and produced by the team at www.BestCarAudio.com. Reproduction or use of any kind is prohibited without the express written permission of 1sixty8 media.